Personal consumer and financial information is under constant threat from cyber thieves around the globe. There are plenty of cases where major databases containing critical consumer information have been involved in data breaches because of present vulnerabilities. In 2004, the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) was founded by leading credit card companies Visa, Mastercard and others, in response to a dramatic rise in payment fraud. The council established mandatory security procedures that all who use their payment facilities must adhere to. Although technology continues to develop ever more sophisticated security measures, there are still lucrative tactics used by thieves to exploit consumer data by stealing their money and personal identities. The stolen data is then sent to such places where exploitation is easy and there is no practical enforcement of the law. To secure consumer data, businesses need to comply with the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard (DSS). By following the guidelines of PCI DSS, companies, software testers and individuals, can ensure that consumer payment card data is as secure and safe from exploitation as possible.

Exposing the Risks in Payment
Whenever a transaction is made, many elements are involved in the process. Devices, software, hardware, network, and service providers, are needed to move money from one place to another. Each channel is theoretically exploitable by cyber thieves, and it is important for businesses to make sure that the appropriate levels of security control are in place to protect consumer data.
PCI Standards Overview
PCI standards prescribe a set of rules and guidelines for all organizations that store or process cardholder data, and precise technical requirements are defined for three important sectors; software developers, manufacturers, and merchants. Merchants are the most vulnerable group when it comes to losing consumer data.
How PCI Security Standards relate to each area is shown in the following section:
- PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): This standard is the core component and is designed for merchants and processors. It defines various controls and processes that need to be in place for the protection of cardholder data.
- Payment Application Data Security Standard (PA DSS): This standard is for software developers or organizations that build and sell software for payment processing. The code directs that only secure and approved payment processing is used in the application.
- Personal Identification Number (PIN) Transaction Security Requirement (PTS): This standard is for manufacturers of card payment devices that businesses use at the point of sale. It is directed that only such devices that comply with PTS are used.
Merchant PCI DSS Levels
Merchants are classified into four compliance levels, with adherence to PCI guidelines being mandatory for all. The four levels are differentiated on the basis of transaction volume over a year, but the exact specification requirements will often vary according to the card company used. The details should be used only as a basic guide and we suggest that those needing exact information undertake further research regarding specific card issuer.
Level 1: This level is for those merchants who process above 6 million transactions over the course of one year, and for those who have experienced a breach of data or cyberattack that resulted in the compromise of cardholder data. Due to such a huge number of transactions, Level 1 merchants are required to carry out extra measures to safeguard their processing system. Scans will probably be required to assess vulnerability every 90 days and a security audit after a year, but businesses need to check for the latest requirements before setting procedures in place
Level 2: Merchants who process transactions between 1 million to 6 million per year belong to this category. PCI guidelines require a quarterly vulnerability scan to spot weak points but again, check for the latest requirement updates before setting schedules.
Level 3: This level refers to merchants who process 20,000 to 1 million transactions per year. Check PCI guidelines for their current vulnerability scan requirements.
Level 4: This is the level for those merchants who process less than 20,000 transactions per year and for those who process up to 1 million e-transactions per year. Validation requirements vary according to the acquiring bank used by the merchant.
Besides conducting a vulnerability scan on a quarterly basis and any other required checks, audits, and verifications, it is recommended the Self Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) is completed on an annual basis to keep compliance up to date.
Payment process Overview
Any payment made by card would usually go through the following processes in order for the merchant to receive their revenue. This process is usually handled by the payment gateway and merchant bank:
- Authorization: The cardholder allows merchants to proceed with the transaction. Authorization is granted to the merchant by the card issuer so the payment can be processed.
- Clearing: Information is then exchanged between the bank and card issuer over the network.
- Settlement: Finally, the transaction is credited in the merchant’s account and debited from the cardholder’s account.
Guidelines for Securing Cardholder Data
PCI Security Standards guidelines suggest two methods for fixing any loopholes in the process to ensure the safety of cardholder data.
- Technology: Integrate software, hardware, and third-party services to form an application for protecting cardholder data.
- Security: A comprehensive process to define procedures and guidelines for making the system optimally free of vulnerability.
It is important for organizations to prevent malware and viruses entering the system and stealing cardholder data. To this end, technology and security go hand in hand, with PCI advising both a technology-oriented and process-oriented solution. With technology, approved and trusted antivirus software should be on all systems that could be affected by malicious attacks that usually come from other systems and servers. Regarding process, organizations should make sure that all anti-virus software is active, up to date, and efficiently generating logs.
Quality Assurance Process
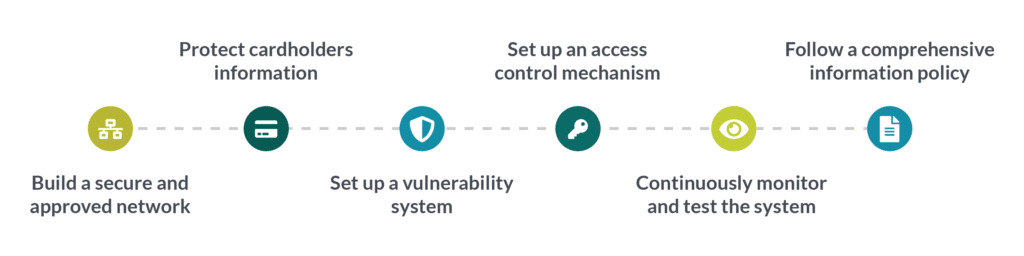
It is necessary for online businesses, especially e-commerce websites, to comply with regulations in order to receive payments via cards for the services they provide. As is evident, card payments come under the PCI DSS regulation, and there are six major compliancy requirements that need to be fulfilled. Following is the summary of those requirements:
- To build a secure and approved network
- To protect cardholders and consumers’ critical information
- To set up a vulnerability system (such as reliable anti-virus)
- To set up an access control mechanism
- To continuously monitor and test the system end-to-end
- To follow a comprehensive information policy written according to the business needs
Businesses can comply with PCI by not retaining cardholder information. Point-of-sale (POS) systems can be utilized that don’t normally not retain consumer data. Alternately, a third-party payment system can also be used but under this format, businesses still remain responsible for the consumer data and their websites need to be secure during the payment process within the following three areas.
1. Secure Web Host Environment
For accepting the payment from cardholders, websites should use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption and the hosting server should be reliable. Before choosing a hosting facility, organizations must make sure that their server, shopping cart, and hosting plan should be in compliance with PCI standards. Instead of using a shared hosting program, the organization should go with a dedicated hosting program which will make sure that their business alone will use the particular server for data storing. It is quite common for payment gateways to provide functionality to help card data to be accepted in a secure way, this could be by a hosted page or transparent redirect for example and the main aim of this is often to prevent any card data being processed by the server. This may also help with obtaining the correct PCI compliance certification, but there will still be standards that your own servers still need to meet.
2. Shopping Cart
It is necessary to choose reputable shopping cart software because you are not only protecting your cardholders’ data but must also protect your business as well. Hence the objective should be to choose a shopping cart that is PA DSS compliant. This will ensure that the shopping cart application is robust enough to block any malicious attacks and will protect the data effectively.
3. Organization Employees
Upper-level businesses tend to understand the importance of data protection, but it is vital the organization imparts their objective to staff who deal directly with consumer data. All employees must be made aware of their responsibility to protect cardholder data and that they should not, under any circumstance, store the data on an unauthorized machine. Organizations must also ensure that all machines, handheld devices, wired and wireless devices, should only be connected to the dedicated server that also has an up to date antivirus program and firewall. Additionally, all access should be password protected.
Recommendations for Security Best Practice
Organizations need to ensure that their technology and processes comply with PCI standards and guidelines. These guidelines may include the following:
- Install a Firewall: The primary protection between vulnerabilities and the whole system is the firewall. There should be no unauthorized access to the firewall and appropriate measures should be taken to maintain the integrity.
- A strong Password: Organizations must ensure that they do not use default passwords for their system, but instead, strong individual passwords should be created because they are vital for security. Due to the increased use of sophisticated Brute Force, Dictionary and Rainbow table algorithm password cracking software, randomly generated passwords containing a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers and special characters, should be used. The easier the password is to remember, the higher the chance of it be unencrypted and stolen by cyber thieves.
- Data Protection: Organizations are compliant by default with the PCI if they do not store cardholder data. However, if payment card data is stored, a regular data disposal schedule needs to be set up, even if the data is encrypted, so stored data can be safely and often deleted.
- Anti Virus Software: Criminal vulnerabilities such as Trojan horses, malware, and viruses, can enter the system via emails and a number of other online activities which may unwittingly be introduced by employees. PCI directs organizations to have trusted antivirus software in place and for employees to restrict their activities online when using the dedicated system directly linked with the payment process.
- Authorization: To support accountability, an organization should only grant only enough access to employees that will allow them to perform their specific jobs. For this purpose, PCI suggests that each employee should have a unique ID, so every step can be traced back if a problem arises.
- Frequent Monitoring: System activity logs are a reliable source for determining the exact nature of problem. PCI suggests that all entries for each possible breach event must be logged in the database with all relevant details, and should be available on-demand without integrity being compromised.
- Frequent Security Testing: It is crucial for the organization to frequently test their systems for any vulnerability with the help of experienced security professionals, especially when there is a new deployment and changes have been made to the existing system.
- How to test? Vulnerability scanning of the entire system helps the organization to automatically detect vulnerabilities, according to PCI Security Standards. For the purpose of scanning only, an Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV) can be brought in to perform a network scan, as well as make sure that all the requirements of PCI DSS are fulfilled.
- What to test? According to PCI guidelines, it is recommended that the entire system for all the wired network, wireless network, security, and system files are tested.
- When to test? PCI dictate that organizations test their systems every 90 days or after any change takes place anywhere in the system. For external scanning, ASV is required, but for internal scanning, you need experienced security personnel for penetration testing.
PCI Compliance Testing Tools and Services
It is evident that despite government policies and strict rules and regulations, cyber thieves still try to steal consumer data. There are organizations that provide specialized tools and services for supporting payment processes in complying with PCI DSS requirements.
- Security Metrics: Security Metrics provides specialized services for compliance and data security. They have a dedicated team for PCI Audits, which helps the businesses to secure their internal and external payment environment.
- Comodo: Comodo is another established name in the industry that offers plenty of services in the domain of compliance and security. They also offer anti-virus software and firewalls. Their collective list of products helps businesses with the security of payment processes secure data at all levels.
- Solarwinds: This is another product that provides various tools for PCI compliance, with customization available to suit your business. They offer a free trial as well so you can analyze how their products manage vulnerabilities and learn how their tools work before making a financial commitment.
Conclusion
PCI compliance is a necessary and ongoing commitment. Large organizations must continuously monitor their processes to make sure that consumer data remains in safe hands, because of doing so can bring large fines imposed for negligent security breaches. Following such an event, retaining consumers will most likely be impossible because former customers will move on to use the services of your competitors instead.